Said El Mansour Cherkaoui, Ph.D. – Email contact: saidcherkaoui@triconsultingkyoto.com
Oct 22, 2024, updated on Oct 26, 2024
This article will define the main steps that have shaped the progress of the BRIC, BRICS, and now BRICS + 2024. The main aspects are presented with their direct impact on the international relations between economic nations. The BRICS + as a new group of emerging countries have in their beginning concentrated on having an alternative space where they can build between the founding members direct communication on their trade and financial relationships. The BRIC acronym stands for #Brazil, #Russia, #India, #China, and #SouthAfrica. The setting of the related structure was materialized making the addition of an African Member South Africa transforming the BRIC into BRICS. This step has allowed the BRIC Club to be a Community of Nations that are representative of continents and regions of the world that can share common grounds of needs and seek common solutions to the challenges raised and created by the Western Advanced Economies.
A sort of new differentiation was put in place for middle economic nations to be distinctive from the rest of countries considered as Subcapitalit economies that had no international organ representing their interests in common means and ways of defense or expression. The BRICS filled this gap and started building structures to substitute them for what the Western Advanced Economies have created since the end of the Second World War to maintain a certain discipline and control of the international arenas of trade, business, finance, and culture as well as direct diplomatic relationships between their members. This evolution imposed on the BRICS to become and to be more representative to be able to use the structures built and to create more credibility for their actions and objectives. The present 16th BRICS Summit in Kazan is effectively the real translation and expression of such role and function that its founding members are pursuing and trying to materialize in the sense of reinforcing a response to Multipolarism and Multilateralism as new forms of intra and international structuring of the relationship between the countries of the South and those of the North.
In the following text, you will read about the evolution of the BRICS its transformative path, and its continual adaptation to new challenges erupting on the international scene. The founding members of the BRICS with China at the forefront of the Group, are seeking to increase their weight and their propositions to respond and express their approaches which aim at the monopoly played by Western-based organizations in defining the direction of the World economy, the Geostrategic interests and the Economic regulations have been carried since the beginning of the 19th century with the end of the Colonial Prohibitions and Mercantilism and the expansion of Liberalism to the present time of Neoliberalism.
Breaking the Borders of Globalization, Multinationalisation, and Internationalization and Setting New Forms of Supra-Integration
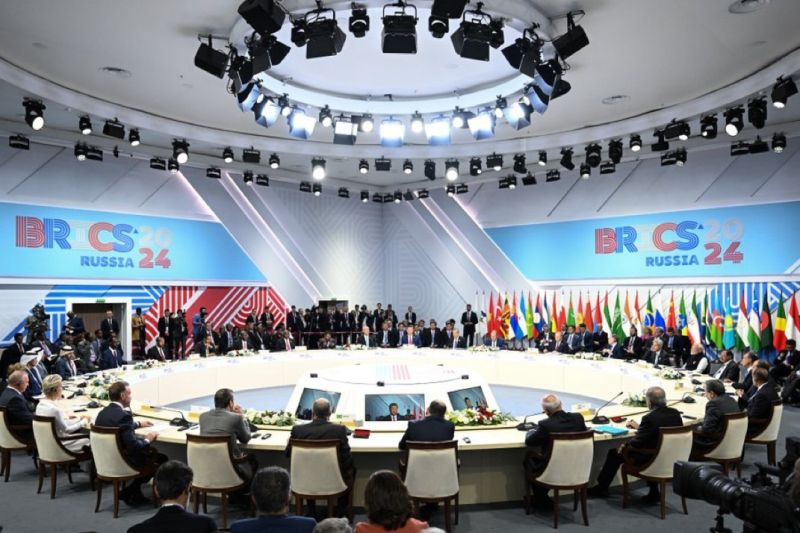
The 16th BRICS Summit in Kazan is being held under the chairmanship of Russia from October 22-24. The Ministry of External Affairs said, “The Summit, themed ‘Strengthening Multilateralism for Just Global Development and Security,’ will provide an important platform for leaders to discuss key global issues.”
Adding New Members to BRICS
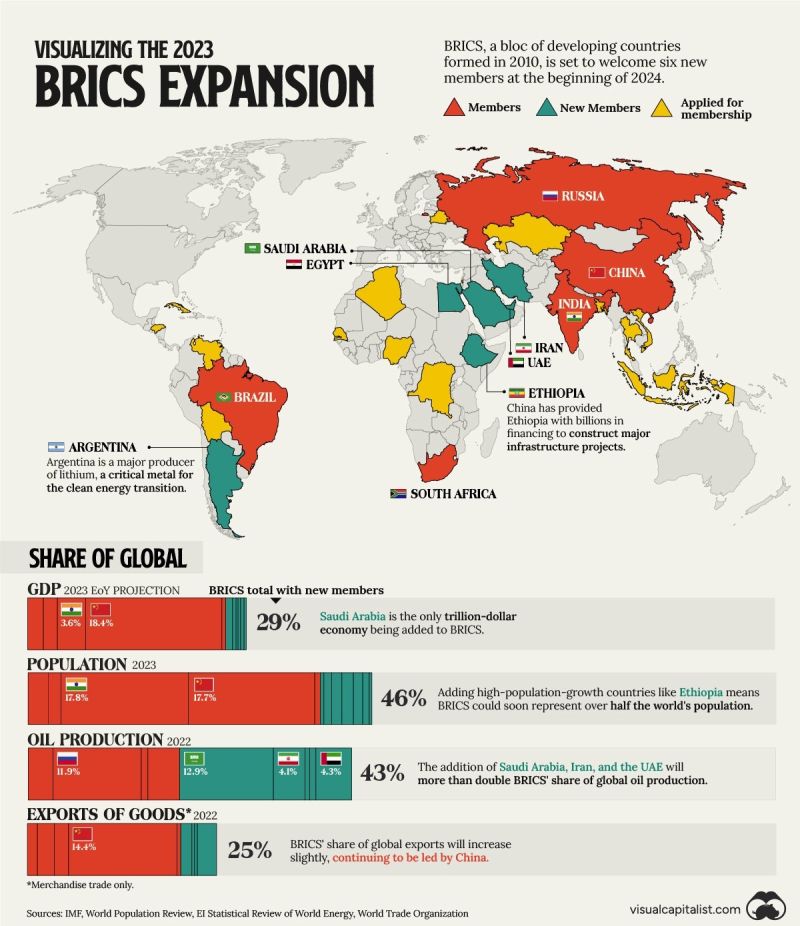
The #BRICS group expanded in early 2024 to include #Iran, the #UnitedArabEmirates, #Ethiopia, and #Egypt. #SaudiArabia was also announced as a new member, though the kingdom has yet to make a final decision on whether to join. Argentinian President Javier Milei, who took office in December 2023 and is steering his country’s geopolitical alignment toward the #US and away from China and Brazil, declined a membership invitation.
The nations still seeking admission include #Malaysia, #Thailand, and #Turkey. Further enlargement could be discussed during this summit in Kazan, Russia, on Oct. 22-24.
What is the impetus for expansion?
The BRICS club of nations almost doubled in size this year, making it a more credible counterweight to the G7. The BRICS group of emerging-market powers has gone from a slogan dreamed up at an #investmentbank to BRICS+ two almost doubled in size in 2024, pairing several major #energy producers with some of the biggest consumers among developing countries and potentially enhancing the group’s economic clout in a US-dominated #world. The push has been driven largely by China, now the world’s pre-eminent industrial power, which is trying to boost its global clout by courting nations traditionally allied with the US. South Africa and Russia have backed the expansion. India was initially hesitant because it was concerned that a bigger BRICS would transform the group into a mouthpiece for China, while Brazil was worried about alienating the West — although both governments eventually agreed to an enlargement.
The Launching Pad of the BRICS
Jim O’Neill, the Chief Economist at Goldman Sachs, created the acronym BRICS in 2001. O’Neill’s research paper, Building Better Global Economic BRICs, proposed that the economic potential of Brazil, Russia, India, and China (BRIC) could make them among the world’s most dominant economies by 2050. O’Neill argued that the growth of these countries could challenge the dominance of the G7, the world’s seven most advanced economies.
The BRICS group of emerging-market powers — the acronym stands for #Brazil, #Russia, #India, #China, and #SouthAfrica — has gone from a slogan dreamed up at an #investmentbank and the Brics two decades ago.

Russia and the U.S. Dollar: A Yoyo Game by the Control of Gold
On June 2024, With the BRICS firmly committed to de-dollarization, Morgan Stanley recently said that the US dollar cannot be dethroned.
On the heels of what Kaddafi was proposing the use of their pricing for gold would serve as the basis for payment for other primary goods including petrol. This claim was the last straw that broke the back of the camel and resulted in his assassination. Almost in a similar line to nationalizing the price of the precious metals, Russia has proposed that BRICS member countries create their own precious metals exchange in a move that could upend the long-established international pricing mechanisms for gold, silver, platinum, and other precious metals. This declaration has sent the price of gold skyrocketing.
The news comes on October 23, 2024, on the heels of Wednesday’s declaration adopted by the leaders of the BRICS countries supporting an increase in the exchange of precious metals between members based on common product quality standards.
At the Kazan summit, Russia proposed to the BRICS countries to create a precious metals exchange, which, according to the authors of the idea, will fundamentally change the principles of pricing in this conservative market.

As stated in the message of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, the declaration of the leaders of the BRICS countries adopted on Wednesday supported an increase in the turnover of precious metals between the countries of the association based on common product quality standards. “The creation of a mechanism for trading metals within the BRICS countries will lead to the formation of fair and equitable competition based on exchange principles,” the Ministry of Finance said in a release.
“The mechanism will include the creation of instruments for price indicators for metals, standards for the production and trade of bullion, accreditation of market participants, clearing and auditing within the BRICS countries, and the participating countries will have a reliable way of stable exchange trading within the association,” said the head of the department Anton Siluanov, quoted in the message.
The Finance Ministry added that they expect the BRICS Precious Metals Exchange “will become a key regulator of prices for precious metals.”

The BRICS club of nations dominated by China almost doubled in size this year 2024, making it a more credible counterweight to the G7. The BRICS is pairing several major #energy producers with some of the biggest consumers among developing countries and potentially enhancing the group’s economic clout in a US-dominated #world. Dozens more countries have expressed interest in joining its ranks.
Who are the New Members of BRICS?
The rise of BRICS (and now BRICS+) reflects a shared belief among important emerging players that the Western-dominated, rules-based international order—and particularly the system of global economic governance—is both stacked against their interests and fundamentally outdated. The #BRICS group expanded in early 2024 to include #Iran, the #UnitedArabEmirates, #Ethiopia, and #Egypt. #SaudiArabia was also announced as a new member, though the kingdom has yet to make a final decision on whether to join. Argentinian President Javier Milei, who took office in December 2023 and is steering his country’s geopolitical alignment toward the #US and away from China and Brazil, declined a membership invitation.
The nations still seeking admission include #Malaysia, #Thailand, and #Turkey. Further enlargement is likely to be discussed at a summit in Kazan, Russia, on Oct. 22-24.
The 16th BRICS Summit in Kazan is being held under the chairmanship of Russia from October 22-24. The Ministry of External Affairs said, “The Summit, themed ‘Strengthening Multilateralism for Just Global Development and Security,’ will provide an important platform for leaders to discuss key global issues.”
What is the impetus for the expansion of the BRICS?
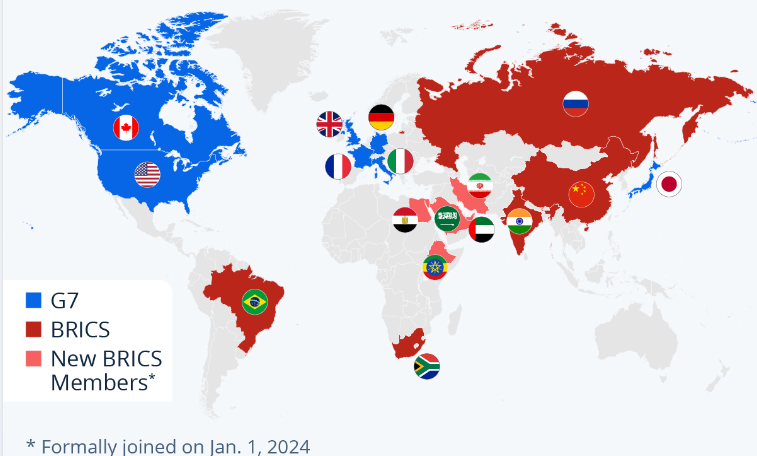
Russian President Vladimir Putin will host the first-ever summit of BRICS+ from October 22 to 24 in the Tatarstan city of Kazan. There, the founding members of BRICS—Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa—will formally welcome into their fold five new members: Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Putin has also invited more than two dozen other countries that have applied for or are considering membership in the expanding club. The gathering is meant to send an unmistakable signal: Despite the West’s best efforts to isolate it, Russia has many friends around the world.
To some in the West, the emergence of BRICS+ suggests something even more ominous—a world that is fragmenting into competing blocs, thanks to intensifying geopolitical rivalry between East and West and growing mutual alienation between North and South. According to this reading, Beijing and Moscow are intent on exploiting some countries’ resentment of the United States and its wealthy world allies to consolidate an anti-Western counterweight to the venerable Group of 7 (G7), a process that is likely to paralyze global cooperation within other multilateral venues.
China’s Energy Tight-Belt Road Initiative
TRI CONSULTING KYOTO TRI CK USA – Said El Mansour Cherkaoui © Said El Mansour Cherkaoui – 9/11/2024 Introduction – China-Africa Cooperation – FOCAC This is a presentation of the relationship of China with Africa depicting several years of interactions that had been developed through indirect and direct investments and technical support provided to the African States by Chinese companies and engineers. China has mastered the … Continue reading China’s Energy Tight-Belt Road Initiative
Global Risk Analysis
TRI CONSULTING KYOTO TRI CK USA – Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Ph.D. ★ Strategic Catalyst Driving U.S.-Morocco-Africa Investment, Trade, and Business Development ★ Senior Policy Adviser in International Affairs ★ Accomplished Public Speaker ★ Distinguished News Executive Editor ★ The recent decline in the United States’ standing in the Arab world and China’s growing influence indeed has significant implications. Let’s break down … Continue reading

China Puzzled by U.S. Trade Economics and Politics System – Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Ph.D. – Said Cherkaoui Ph.D. TRI CK USA – Email: saidcherkaoui@triconsultingkyoto.com 8 27 24 – Oakland – Bay Area of San Francisco – California Trade-wise, The four years witnessed escalating trade tensions culminating in a trade war and sanctions on Chinese technology companies. Since Biden’s election, political and business stakeholders … Continue Reading
China Exports to Russia and Multipolarity of the World
Collage made by Said El Mansour Cherkaoui tracing the USA-China relation since the Presidency of Donald Trump that we consider as the opening of a New Chapter that we are still reading up to now Global Risk Analysis Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Ph.D. ★ Strategic Catalyst Driving U.S.-Morocco-Africa Investment, Trade, and Business Development ★ Senior … Continue reading
Of particular concern is the future of the Group of 20 (G20). Even before BRICS expansion, it had become a microcosm of growing global rifts. A further hardening of these divisions would undercut the G20’s fundamental raison d’être: namely, to help bridge gulfs between—and leverage the capabilities of—important countries that are not inherently or necessarily like-minded.
With the rise of economies like China and India, many countries see BRICS as a platform to counterbalance the influence of traditional Western powers. Recent global conflicts and increased US-China rivalry might push countries towards BRICS as a way to navigate complex geopolitical dynamics.
The push has been driven largely by China, now the world’s pre-eminent industrial power, which is trying to boost its global clout by courting nations traditionally allied with the US. South Africa and Russia have backed the expansion. India was initially hesitant because it was concerned that a bigger BRICS would transform the group into a mouthpiece for China, while Brazil was worried about alienating the West — although both governments eventually agreed to an enlargement.
The 16th BRICS Summit in Kazan is being held under the chairmanship of Russia from October 22-24, 2024. The Ministry of External Affairs said, “The Summit, themed ‘Strengthening Multilateralism for Just Global Development and Security,’ will provide an important platform for leaders to discuss key global issues” and work together to build and implement adequate solutions and adaptable responses to the new challenges that Presiden Xi has called on BRICS members to pursue and realize.
– Build a BRICS committed to peace, and act as defenders of common security.
– Build a BRICS committed to innovation, and act as pioneers of high-quality development.
– Build a BRICS committed to green development, and act as promoters of sustainable development.
– Build a BRICS committed to justice, and act as forerunners in reforming global governance.
– Build a BRICS committed to closer people-to-people exchanges, and act as advocates for harmonious coexistence among all civilizations.
Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Ph.D. – Said Cherkaoui Ph.D.
Email contact: saidcherkaoui@triconsultingkyoto.com
Liberal Pax Americana in the West and Shield of Alliances by the BRICS in the East
Posted on – In 1992, I had a meeting with a European Commissaire at the Boalt Library at the University of California at Berkeley and I conducted an interview about the creation of the European Economic Community and its monetary policies. This interaction was made given that as Adjunct Associate Professor, I introduced for the first time in … Continue reading“ Liberal Pax Americana in the West and Shield of Alliances by the BRICS in the East”
BRICS Fortress to Shield Dollar
Posted on – BRICS AND THE SOUTHERN COUNTRIES FACING THE DOLLAR ECONOMY The acronym BRIC, which initially stood for Brazil, Russia, India, and China, was coined by Jim O’Neill in 2001 when he was chief economist of the multinational investment bank, Goldman Sachs. At the time, the four countries had sustained rates of high economic growth and the … Continue reading “BRICS Fortress to Shield Dollar”
China’s Reinforcing BRICS with the Foundation of Development Bank
Posted on – By Dr. Said El Mansour Cherkaoui – Oct 2, 2015 In June 2014, the BRICS group formed by the so-called emerging economies of Brazil, Russia, India, China and the new member, South Africa had effectively signed a memorandum of understanding aimed at creating a new international financial institution. A year later, these same countries materialized … Continue reading “China’s Reinforcing BRICS with the Foundation of Development Bank”
BRICS Building Financial Great Wall
Posted on – Said El Mansour Cherkaoui World Tour du Monde Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Dr. Said El Mansour Cherkaoui et le Tour du Monde: De Doukkala, Mazagan, El … Continue reading Said El Mansour Cherkaoui World Tour du Monde – REBUILDING MOROCCO New Economic Houses on BRICS and MINT Nouvelles Eco-Demeures en BRICS et Menthe Said El Mansour Cherkaoui – Published … Continue reading “BRICS Building Financial Great Wall”
BRICS and the Building of Financial Great Wall
December 9, 2021 ★ Said El Mansour Cherkaoui, Ph.D. ★ Published on July 1, 2015 – 78 articles published at LinkedIn Great Wall and Great Break Banking Time for BRICS From July 2014 to July 2015, the BRICS group, the new emerging economies of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa signed a Memorandum of Understanding to create…Continue Reading →


Said El Mansour Cherkaoui World Tour du Monde

Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Dr. Said El Mansour Cherkaoui et le Tour du Monde: De Doukkala, Mazagan, El … Continue reading Said El Mansour Cherkaoui World Tour du Monde – REBUILDING MOROCCO
New Economic Houses on BRICS and MINT
Nouvelles Eco-Demeures en BRICS et Menthe


English Version: New Economic Houses on BRICS and MINT
The Financial Times estimated that the seven largest emerging economies can hypothetically be called a new G7: four BRICS members – Brazil, Russia, India and China and three countries of the so-called MINT – Mexico, Indonesia and Turkey, will have a combined GDP of $37.8 trillion in 2014 when calculated at purchasing power parity (PPS).
However, the long established G7 group of industrialized nations: Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the UK and the US are expected to have an output of $34.5 trillion.
More details at this website: http://en.itar-tass.com/economy/753399
Version Française: Les nouvelles puissances économiques du monde Bâtie sur BRICS et à la Menthe
Le Financial Times estime que les sept plus grandes économies émergentes peuvent hypothétiquement être appelés une nouvelle G7: quatre membres du BRICS – Brésil, Russie, Inde et Chine et trois pays de la soi-disant MINT – Mexique, l’Indonésie et la Turquie, aura un PIB combiné de $ 37,8 trillions en 2014 lorsqu’il est calculé à partir de la Parité de Pouvoir d’Achat (PPA).
http://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parit%C3%A9_de_pouvoir_d’achat
Cependant, le groupe du G7 établi de longue date par les pays industrialisés: le Canada, la France, l’Allemagne, l’Italie, le Japon, le Royaume-Uni et les États-Unis devraient avoir un total de seulement $ 34,5 trillions.
http://en.itar-tass.com/economy/753399

Building New Economic World Powerhouses on BRICS and MINT
Updated on Sep 1, 2015
Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Published Jul 1, 2015
Email: Said El Mansour Cherkaoui
BRICS and the Building of Financial Great Wall
GREAT BREAK TIME FOR BRICS:
From July 2014 to July 2015, the BRICS group, the new emerging economies of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa signed a Memorandum of Understanding to create a new international financial institution capitalized with $200 billion of liquidity. This banking organization was projected to act as BRICS Development Bank with $100 billion along with a reserve currency pool worth over another $100 billion.
On July 2015, in China, the New Development bank, also known as the BRICS Bank, has been approved by the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress during its meetings that are actually taking place until July 1, 2015. India and Russia had already agreed on this creation and South Africa is expected to present ratification documents in July during a meeting of BRICS countries in the Russian city of Ufa.
THE BRICS FACTORY OF GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT:
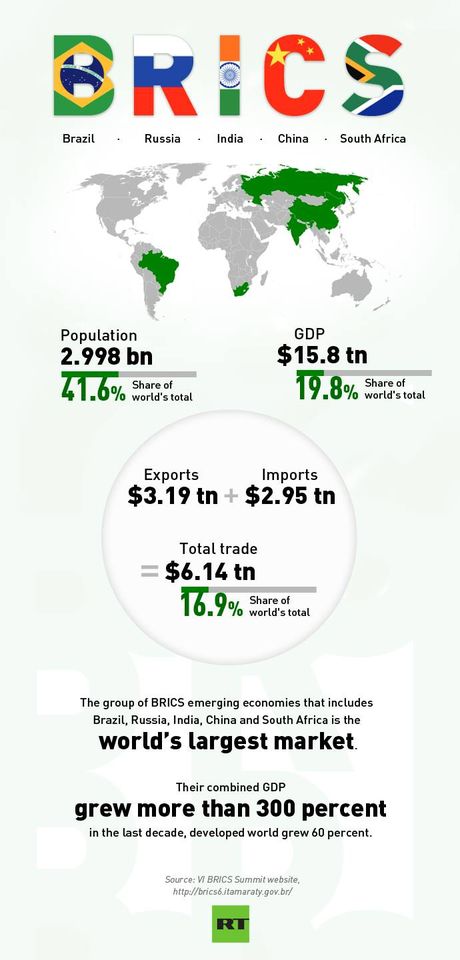
In terms of demographic and economic standards, the BRICS are becoming heavy weights challengers for the New World Order inherited from the Presidency of Father Bush. The group BRICS has 42 percent of the world’s population and roughly 20 percent of the world’s economy based on gross domestic product, and 30 percent of the world’s GDP based on purchasing power parity. * The total trade between the BRICS’ countries is $6.14 trillion, or nearly 17 percent of the world’s total. They also account for 11 percent of global capital investment. China, India and Brazil are also ranked among the largest economies in the world with more than $2 trillion, €1.25 trillion by nominal GDP.
In 2015, the members of this privileged “Elite” club were the United States, China, Japan, Germany, France, the United Kingdom and India. Their ranking in respect to respective GDP in trillions of U.S. dollars is the following: USA $18.1 – China $11.2 – Japan $4.2 – Germany $3.4 – U.K. $2.9 – France $2.5 – India $2.3 – Brazil $1.9 – Italy $1.8 – Canada$1.6.
THE STRUCTURE OF NEW BRICS DEVELOPMENT BANK:
Each member of the BRICS will have a seat for their Finance Minister or Central Bank Chair at the Bank’s Representative Board. The other innovation is that membership is not just limited to BRICS economies such is the case in other international financial institutions. The BRICS Bank will be headquartered in Shanghai, with India presiding it during the first year, and Russia serving as the chairman of the representatives. During the BRICS and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) summits in the Russian city of Ufa, Anton Siluanov has been appointed Board Chairman of the New Development Bank, he is the current Russian Finance Minister. Similarly, it has been agreed that an African regional center of the NDB bank will be established in South Africa.
In recent interview conducted by RT, the New Development Bank president Kundapur Vaman Kamath declared a “significant part” of the bank’s activity could be carried out in local currencies. “I have not applied my mind as to what effect it will have on other currencies. But as far as our local currencies are concerned, our own countries are concerned, that will substantially reduce any exchange risk.” He also projected that by April 2016 the New Development Bank will issue its first loan.
Mr. Kamath added: “I think clearly setting up of this bank is also a signal that developing countries are now able to stand on their feet in their own way and set up their own institutions. We are really looking at expanding the membership base in the future.” In this perspective, joining the Development Bank remains open to other emerging countries, such as Mexico, Indonesia, or Argentina, once it sorts out its debt burden.
The initial funding came from each BRICS member that will contribute an equal share in establishing a startup capital of $50 billion while the full participation is $100 billion. This capitalization represents a crisis lending fund and is called the Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA). China contributed with $41 billion while Russia, Brazil and India will add in $18 billion, and South Africa, the newest member, will contribute $5 billion. The contribution of 39.5 percent will give China the largest voting rights.
On the 7/9/2015, Russian President Vladimir Putin is meeting BRICS leaders in an expanded format at the BRICS and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) summits in the Russian city of Ufa which took place on July 8-10, 2015. The Summit in the Russian City of Ufa become the cradle for the official launch of the New Development Bank and the designation of its leaders. in the same perspective, the BRICS countries agreed to put in place a $100bn reserve currency pool which aims to protect the member states – the emerging economies of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa – from currency volatility shocks. This is one of the reasons, the summits agreed that the association will start using their local currencies for mutual settlements quite soon.
In fact, the continuity of the financial imbalances of the western economies added to the unpredictability of their financial institutions and their budgetary deficits had added more concerns to the BRICS members and have motivated them to sustain the creation of the New Development Bank, an alternative and a supplement to existing international “hard currency” financial institutions.
THE NEW ALTERNATIVE TO THE UNION OF WESTERN BANKS:
The idea behind these financial moves is to create structures that will help to lessen dependency on the West and to create a more multi-polar world. Other implications are a design to protect against the instability and the fluctuations of the Western based currencies. The BRICS BANK is sought to provide also financial means and resources to counter the influence of Western-based lending institutions and the US Dollar, especially at the wake of the current financial turmoil traversing the western economies and the regional conflicts generated by the consequent race for the natural resources around the globe.
Within such frame, the long domination of the US Dollar since the signing of Bretton Woods Agreement and the Nixon Administration’s creation of the Petro-dollars (1973 oil crisis) are starting to show some fissures and weakness in the resolution, remittance and refinancing of international transactions.
Furthermore, the western-based banking system and the recent Libor scandal and other related fraudulent behaviors and abuses coupled had increased the reluctance of Emerging economies to continue to be financed through a system that rely only on lending volume as the key metric for success. Similarly, the development and the integration of technology-oriented methods of resolution and transfer of assets and financial denominations have added more determinations to the Emerging economies to establish their own channels to finance their infrastructures and funnels directly their funds without intermediaries. These technological advances have also facilitated the consultation and the planning of infrastructural projects to be financed as joint development ventures by the BRICS economies for their own countries and for the rest of the developing world.
Additionally, the need of alternative global financial instruments is increasing given that the trade is bilaterally developed among emerging economies and between them and the rest of the developing world. For these reasons, the financial institutions and facilities offered by western societies such as the IMF, the World Bank and the OPIC and their regional agencies are considered as organizations dominated by western shareholders which add more challenges for projects oriented toward the development of national resources and the related infrastructure. Within such perspective, the other bank being promoted by China as an alternative to existing development institutions, such as the IMF and the World Bank, is the new Asian Development Bank, known as the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, that was established in October 2014. Britain and Germany are listed among its 57 member states.
To avoid such hurdles and to reduce cost and time in terms of realizations, the emerging economies are developing regional free trade blocs and treaties that are engaging their financial resources as well. For these reasons, the Members of BRICS are seeking to reinforce bilateral trade relations without relying on the evaluation or the approval by Western based decision making. The other aspect is the total fees charged by the related lending institution and the influence of the dollar in the development of the international trade of commodities and primary goods.
The implications of all these new forms of competitiveness at the level of financial transactions and their far-reaching impact on the balance of payments, especially the current accounts of the countries concerned, it is without equivoque that new currencies are going to be emerging within certain trading blocs before to reach an international acceptance. The establishment of these regional banking institutions that aim to be a global player are the first signs of such move.
Additional Notes for Clarification:
For more on the BRICS and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) summits in the Russian city of Ufa, see the video on the following link:
http://rt.com/on-air/putin-meets-brics-leaders/
N.B.: * The aforementioned indicators are reflective of tendencies and not realities of economic situations and social conditions. For this reason, they have to be considered as reflective of selective and comparative performances given the fact that the world economy can be defined, estimated, evaluated, but also can be expressed in various other forms and indications. “It is unclear, for example, how many of the world’s 7.13 billion people have most of their economic activity reflected in these [aforementioned] valuations.”
Any comments or needs can be directly addressed to Dr. Said El Mansour Cherkaoui: saidcherkaoui@triconsultingkyoto.com
GREAT BREAK TIME FOR BRICS:
Said El Mansour Cherkaoui, July 1, 2015 – 79 articles – Email: Said El Mansour Cherkaoui
From July 2014 to July 2015, the BRICS group, the new emerging economies of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa signed a Memorandum of Understanding to create a new international financial institution capitalized with $200 billion of liquidity. This banking organization was projected to act as BRICS Development Bank with $100 billion along with a reserve currency pool worth over another $100 billion.
On July 2015, in China, the New Development bank, also known as the BRICS Bank, has been approved by the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress during its meetings that are actually taking place until July 1, 2015. India and Russia had already agreed on this creation and South Africa is expected to present ratification documents in July during a meeting of BRICS countries in the Russian city of Ufa.
THE BRICS FACTORY OF GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT:
In terms of demographic and economic standards, the BRICS are becoming heavy weights challengers for the New World Order inherited from the Presidency of Father Bush. The group BRICS has 42 percent of the world’s population and roughly 20 percent of the world’s economy based on gross domestic product, and 30 percent of the world’s GDP based on purchasing power parity. * The total trade between the BRICS’ countries is $6.14 trillion, or nearly 17 percent of the world’s total. They also account for 11 percent of global capital investment. China, India and Brazil are also ranked among the largest economies in the world with more than $2 trillion, €1.25 trillion by nominal GDP.
In 2015, the members of this privileged “Elite” club were the United States, China, Japan, Germany, France, the United Kingdom and India. Their ranking in respect to respective GDP in trillions of U.S. dollars is the following: USA $18.1 – China $11.2 – Japan $4.2 – Germany $3.4 – U.K. $2.9 – France $2.5 – India $2.3 – Brazil $1.9 – Italy $1.8 – Canada$1.6.
THE STRUCTURE OF NEW BRICS DEVELOPMENT BANK:
Each member of the BRICS will have a seat for their Finance Minister or Central Bank Chair at the Bank’s Representative Board. The other innovation is that membership is not just limited to BRICS economies such is the case in other international financial institutions. The BRICS Bank will be headquartered in Shanghai, with India presiding it during the first year, and Russia serving as the chairman of the representatives. During the BRICS and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) summits in the Russian city of Ufa, Anton Siluanov has been appointed Board Chairman of the New Development Bank, he is the current Russian Finance Minister. Similarly, it has been agreed that an African regional center of the NDB bank will be established in South Africa.
In recent interview conducted by RT, the New Development Bank president Kundapur Vaman Kamath declared a “significant part” of the bank’s activity could be carried out in local currencies. “I have not applied my mind as to what effect it will have on other currencies. But as far as our local currencies are concerned, our own countries are concerned, that will substantially reduce any exchange risk.” He also projected that by April 2016 the New Development Bank will issue its first loan.
Mr. Kamath added: “I think clearly setting up of this bank is also a signal that developing countries are now able to stand on their feet in their own way and set up their own institutions. We are really looking at expanding the membership base in the future.” In this perspective, joining the Development Bank remains open to other emerging countries, such as Mexico, Indonesia, or Argentina, once it sorts out its debt burden.
The initial funding came from each BRICS member that will contribute an equal share in establishing a startup capital of $50 billion while the full participation is $100 billion. This capitalization represents a crisis lending fund and is called the Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA). China contributed with $41 billion while Russia, Brazil and India will add in $18 billion, and South Africa, the newest member, will contribute $5 billion. The contribution of 39.5 percent will give China the largest voting rights.
On the 7/9/2015, Russian President Vladimir Putin is meeting BRICS leaders in an expanded format at the BRICS and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) summits in the Russian city of Ufa which took place on July 8-10, 2015. The Summit in the Russian City of Ufa become the craddle for the official launch of the New Development Bank and the designation of its leaders.
In the same perspective, the BRICS countries agreed to put in place a $100bn reserve currency pool which aims to protect the member states – the emerging economies of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa – from currency volatility shocks. This is one of the reasons, the summits agreed that the association will start using their local currencies for mutual settlements quite soon.
In fact, the continuity of the financial imbalances of the western economies added to the unpredictability of their financial institutions and their budgetary deficits had added more concerns to the BRICS members and have motivated them to sustain the creation of the New Development Bank, an alternative and a supplement to existing international “hard currency” financial institutions.
THE NEW ALTERNATIVE TO THE UNION OF WESTERN BANKS:
The idea behind these financial moves is to create structures that will help to lessen dependency on the West and to create a more multi-polar world. Other implications are a design to protect against the instability and the fluctuations of the Western based currencies. The BRICS BANK is sought to provide also financial means and resources to counter the influence of Western-based lending institutions and the US Dollar, especially at the wake of the current financial turmoil traversing the western economies and the regional conflicts generated by the consequent race for the natural resources around the globe.
Within such frame, the long domination of the US Dollar since the signing of Bretton Woods Agreement and the Nixon Administration’s creation of the Petro-dollars (1973 oil crisis) are starting to show some fissures and weakness in the resolution, remittance and refinancing of international transactions.
Furthermore, the western-based banking system and the recent Libor scandal and other related fraudulent behaviors and abuses coupled had increased the reluctance of Emerging economies to continue to be financed through a system that relay only on lending volume as the key metric for success. Similarly, the development and the integration of technology-oriented methods of resolution and transfer of assets and financial denominations have added more determinations to the Emerging economies to establish their own channels to finance their infrastructures and funnels directly their funds without intermediaries. These technological advances have also facilitated the consultation and the planning of infrastructural projects to be financed as joint development ventures by the BRICS economies for their own countries and for the rest of the developing world.
Additionally, the need of alternative global financial instruments is increasing given that the trade is bilaterally developed among emerging economies and between them and the rest of the developing world. For these reasons, the financial institutions and facilities offered by western societies such as the IMF, the World Bank and the OPIC and their regional agencies are considered as organizations dominated by western shareholders which add more challenges for projects oriented toward the development of national resources and the related infrastructure. Within such perspective, the other bank being promoted by China as an alternative to existing development institutions, such as the IMF and the World Bank, is the new Asian Development Bank, known as the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, that was established in October 2014. Britain and Germany are listed among its 57 member states.
To avoid such hurdles and to reduce cost and time in terms of realizations, the emerging economies are developing regional free trade blocs and treaties that are engaging their financial resources as well. For these reasons, the Members of BRICS are seeking to reinforce bilateral trade relations without relying on the evaluation or the approval by Western based decision making. The other aspect is the total fees charged by the related lending institution and the influence of the dollar in the development of the international trade of commodities and primary goods.
The implications of all these new forms of competitiveness at the level of financial transactions and their far-reaching impact on the balance of payments, especially the current accounts of the countries concerned, it is without equivoque that new currencies are going to be emerging within certain trading blocs before to reach an international acceptance. The establishment of these regional banking institutions that aim to be a global player are the first signs of such move.
Unfortunately, the Fed’s first increase was a response to the financial obstruction of the UK economy but was met with OPEC’s decision to cut oil production, Russia’s decision to only accept rubble as a means of payment and the decision of the Chinese to make the payment only with the Yuan for all external transactions.
The conglomeration of all these geo-economic actions made the dollar the first higher than the euro in the international market while it also increased its vulnerability to emerging markets as it impacted more than 60% debt-ridden countries that are on the verge of default with Zambia, Sri Lanka and Ghana at the forefront of full default.
The recession was no longer on the periphery of Western economies, it was spreading beyond the surge in inflation of energy, commodities and the accessibility of basic foodstuffs by many countries.
Also, Japan has always played the role of antechamber and echo chamber for the American economy since the Reaganomics and Economic School of the Chicago Boys.
These changes have motivated producers of oil in the middle east to advocate change of direction for the OPEC and to seek payment alternatives than the dollar which is a kind of renegating on the era of the petrodollars. Within such scope, following the example of Iran, the hydrocarbon-exporting states of the Gulf Cooperation Council looked for alternative methods and means of payments for their energy production which can afford them “to broaden their ability to transact within both dollarised and de-dollarised zones of the global economy. While these states remain firmly embedded in the US-led economic and security architecture, they still see some advantages in reducing their reliance on the US and its currency.”
BRICS Fortress to Shield Dollar August 13, 2023 In “BRICS”
BRICS piece by piece building peace: Lula meeting Xi and Wilma at the Bank
Posted on – Brazil to Be or not to Be Peace-Maker in BRICS Brazil’s President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva is scheduled to arrive in Shanghai on Tuesday, after a March visit was rescheduled due to illness. He will meet with Chinese President Xi Jinping on Friday 4/14/2023. While trade will dominate the agenda, geopolitics are steadily creeping in. Lula’s entourage includes numerous agricultural … Continue reading “BRICS piece by piece building peace: Lula meeting Xi and Wilma at the Bank
Analyse de BRICS sans y ajouter aucune Brique
Posted on – La prééminence des banques britanniques telles que Barings et Rothschild Maison de courtage et des banquiers qui retracent leurs profits dans le commerce des armes contingent du commerce mercantiliste du colonialisme ibérique en Amérique latine. Le changement de l’épicentre du commerce mondial avait provoqué des pertes fonctionnelles continuelles à ces systèmes bancaires et monétaires identifiés dans … Continue reading “Analyse de BRICS sans y ajouter aucune Brique”
Brazil – Africa and Lula
Posted on – Publications and Research on Brazil by Dr. Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Originally published October 31, 2022, with updates on information up to 3/16/2024 Said El Mansour Cherkaoui – support@triconsultingkyoto.com Brazilian President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva – also known as Lula da Silva or simply Lula, is the 39th and current president of Brazil. In 2023, President Lula … Continue reading “Brazil – Africa and Lula
China Global Strategy Built with BRIC and BRI
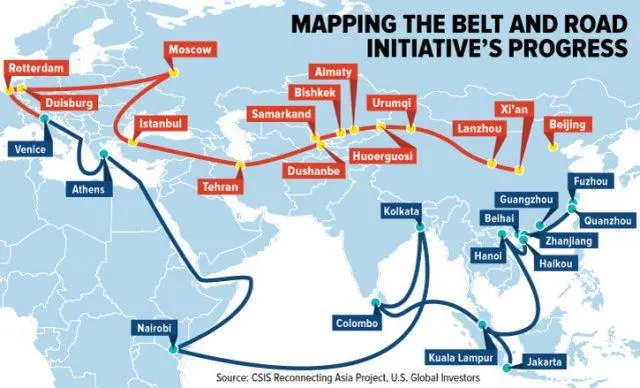
Posted on – Extract: Rooted in history, the BRI carries forward the Silk Road spirit At around 140 BC during China’s Han Dynasty, Zhang Qian, a royal emissary, made a journey to the West from Chang’an (present-day Xi’an in Shaanxi Province), opening an overland route linking the East and the West. Centuries later, in the years of the … Continue reading
Belt and Road Initiative – BRI
Posted on – The Belt and Road Initiative: A Key Pillar of the Global Community of Shared Future / Home / 2023年10月11日 / Belt and Road Initiative, BRI, China, finance, 一带一路, 中国, 带路, 融资 The State Council Information Office of the People’s Republic of China October 2023 Contents Preamble III. Promoting All-Round Connectivity in Multiple Fields Conclusion Preamble Over two millennia ago, inspired by a sincere wish for friendship, our … Continue reading “Belt and Road
World Economy in Mutation Mood
Posted on – TV Shows and Games in America Applied Around the Financial World This turmoil is just the first storm in a glass of wine shared between the banking system and the financial sector hold in hostage by the sanctions on Russia, the rise of alternative currency and the fall of dollar, the skyrocketing of the Federal … Continue reading “World Economy in Mutation Mood”
Western-led International Order Versus Eastern Driven Nationalism
Posted on – Turning Point for the World Order: Publications by Said El Mansour Cherkaoui China – Africa: Diplomatic Multipolarity and Business Regionality As of 2021, China is estimated to hold at least 21% of all African debt. In August 2022, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the… China Affairs by Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Contact Said El … Continue reading “Western-led International Order Versus
New World Economic Individualization
Posted on – New World Economic Individualization End of Globalization by the Acceptation of State Subsidization National Security, Supply-Chain Resiliency and Technology Leadership. New World Economic Individualization: National Security, Supply-Chain Resiliency and Technology Leadership and Direct confrontation has never solved anything besides selling weapons and creating a memory of fears that keep buying weapons as a way to reduce … Continue reading“New World Economic
Liberal Pax Americana in the West and Shield of Alliances by the BRICS in the East October 9, 2023 In ” European Central Bank”
Africa Decade of Geostrategic Rivalries
Posted on – 29 juillet 2022 Diplomatic Valse around Africa and Target of East and West Charms The Russia – Ukraine conflict had also exacerbated the competition in Africa between the United States, China, the European Union and Russia. Each is actually pursuing an orientation that is an attempt of correction and reinforcement which has evolved in frequent … Continue reading “Africa Decade of