
Morocco Background
Morocco is recognized as a top market reformer in the Middle East and North Africa. The nation has emerged as a commercial hub as a result of its economic reforms, investment incentives, competitive costs of production, modern banking processes, strong laws to protect intellectual property, and proximity to major markets. Morocco has a Free Trade Agreement with the United States and an Association Agreement with the European Union (EU). These agreements attract traders looking to enter Morocco, the world’s largest markets (such as the EU and the United States), and the world’s fastest-growing markets (e.g., Africa). The U.S.- – Morocco Free Trade Agreement entered into force in January 2006, eliminating duties on more than 95 percent of all goods and services, and U.S. exports have grown dramatically since then. [source: IFC data]

http://saidcherkaoui24.wordpress.com/said-el-mansour-cherkaoui-moro-maroc/

Morocco’s in 2010-11: Table on Five Pillars
The major resources of the Moroccan economy are agriculture, phosphates, and tourism. Sales of fish and seafood are important as well. Industry and mining contribute about one-third of the annual GDP. Morocco is the world’s third-largest producer of phosphates (after the United States and China), and the price fluctuations of phosphates on the international market greatly influence Morocco’s economy. Tourism and workers’ remittances have played a critical role since independence. The production of textiles and clothing is part of a growing manufacturing sector that accounted for approximately 34% of total exports in 2002, employing 40% of the industrial workforce. The government wishes to increase textile and clothing exports from $1.27 billion in 2001 to $3.29 billion in 2010.
The services sector accounts for just over half of GDP and industry, made up of mining, construction, and manufacturing, is an additional quarter. The sectors that recorded the highest growth are the tourism, telecoms, and textile sectors. Morocco, however, still depends to an inordinate degree on agriculture. The sector accounts for only around 14% of GDP but employs 40-45% of the Moroccan population. With a semi-arid climate, it is difficult to assure good rainfall and Morocco’s GDP varies depending on the weather. Fiscal prudence has allowed for consolidation, with both the budget deficit and debt falling as a percentage of GDP.
In 2009 Morocco was ranked among the top thirty countries in the offshoring sector. Morocco opened its doors to offshoring in July 2006, as one component of the development initiative Plan Emergence, and has so far attracted roughly half of the French-speaking call centers that have gone offshore and a number of the Spanish ones.
According to experts, multinational companies are attracted by Morocco’s geographical and cultural proximity to Europe, in addition to its time zone. In 2007 the country had about 200 call centers, including 30 of significant size, that employ a total of over 18,000 people.
The economic system of the country presents several facets. It is characterized by a large opening towards the outside world. France remains the primary trade partner (supplier and customer) of Morocco. France is also the primary creditor and foreign investor in Morocco. In the Arab world, Morocco has the second-largest non-oil GDP, behind Egypt, as of 2005.
Since the early 1980s, the Moroccan government has pursued an economic program toward accelerating real economic growth with the support of the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, and the Paris Club of creditors. The country’s currency, the dirham, is now fully convertible for current account transactions; reforms of the financial sector have been implemented; and state enterprises are being privatized.
The high cost of imports, especially of petroleum imports, is a major problem. Another chronic problem is unreliable rainfall, which produces drought or sudden floods; in 1995, the country’s worst drought in 30 years forced Morocco to import grain and adversely affected the economy. Another drought occurred in 1997, and one in 1999–2000. Reduced incomes due to drought caused GDP to fall by 7.6% in 1995, by 2.3% in 1997, and by 1.5% in 1999. During the years between drought, and good rains bumper crops to market. Good rainfall in 2001 led to a 5% GDP growth rate. Morocco suffers both from unemployment (9.6% in 2008), and a large external debt estimated at around $20 billion, or half of GDP in 2002.
Overview of Morocco
Morocco Rankings
Overall Score Read our methodology to see how the scores and rankings were calculated.
| Adventure | 3.1 | #35 |
|---|---|---|
| Citizenship | 0.3 | #70 |
| Cultural Influence | 1.5 | #39 |
| Entrepreneurship | 0.2 | #64 |
| Heritage | 4.4 | #21 |
| Movers | 5.7 | #14 |
| Open for Business | 4.5 | #45 |
| Power | 0.3 | #61 |
| Quality of Life | 1.0 | #57 |
Morocco in Photo

Morocco and United States Trade Relations
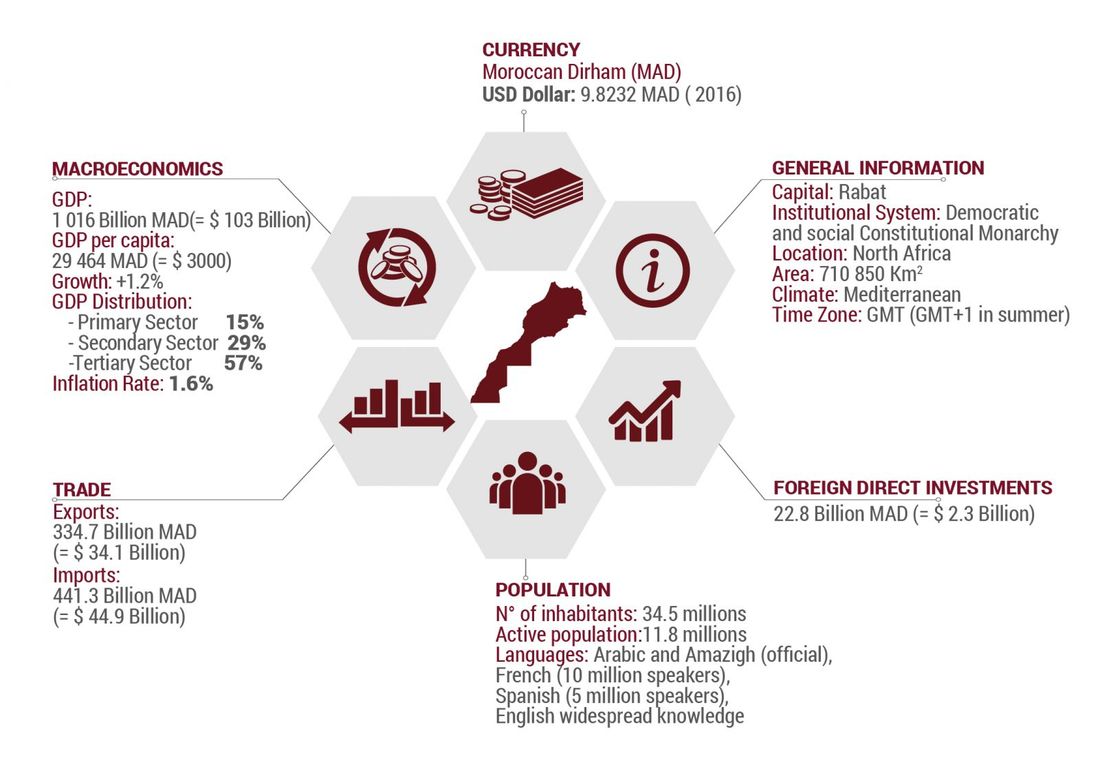
Morocco is located in Northwestern Africa and is slightly geographically larger than California. The capital of Morocco is Rabat, which is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean. Morocco has a population of 34.37 million people and a gross domestic product (GDP) of $100.6 billion. Due to its proximity to Europe along the strategic location as a gateway to Africa, Morocco has created strong trade relationships and promotes an open market economy. In 2015, the US had $304 million in foreign direct investment (FDI) in Morocco.
Morocco and the United States in 2016
The United States is the fourth largest importer of Moroccan goods.
In 2016, the US imported roughly $1 billion worth of goods from Morocco. The largest category of imported goods was chemicals, which made up 36.8% or $375 million of the total. Other imports from Morocco included food manufacturers, apparel manufacturing products, and transportation equipment. In the same year, the United States exported $1.86 billion worth of goods to Morocco, which was an increase from the previous year. In the same year, the United States exported $1.86 billion worth of goods to Morocco, which was an increase from the previous year.
The main exports to Morocco were transportation equipment (31.6%), agricultural products (15%), and petroleum and coal products (8.7%). Export data pulled from the International Trade Administration (ITA) shows that average US exports to Morocco have more than tripled since the US-Morocco Free Trade Agreement (FTA) went into effect just over a decade ago.
President George W. Bush signed the FTA, the first US free trade agreement with an African country, exactly twelve years ago today; and the agreement went into effect on January 1, 2006.
In the three years before the FTA (2003-2005), US exports to Morocco averaged $482 million; in the past three years (2013-2015), they increased 328 percent to $2.1 billion.
At the state level, Texas claims the spot as the top exporter to Morocco, both in 2015 and on average over the past three years, exporting $510 and $710 million worth of goods, respectively. Other top state exporters when looking at three-year averages include Louisiana, West Virginia, Washington, and California in descending order; considering only 2015, Washington, Louisiana, Virginia and California rounded out the top five following Texas.
When looking at sheer growth in exports since before the FTA, other states emerge as winners. Nevada experienced the biggest boost in exports at a nearly 13,000% increase; Idaho’s exports increased by nearly 11,000%; Montana’s by just over 10,000%; New Mexico by nearly 4,500%; and West Virginia by just under 4,000%.
Morocco has been doing everything right to strengthen and diversify its economy,” said former US Ambassador to Morocco Edward M. Gabriel. “Choosing Morocco as the US’s first FTA beneficiary in Africa was a smart move, and I believe the US will continue benefiting from this strong relationship for years to come.
”Here below, you will find presentations on the California – Morocco Trade and the MAFTA – Morocco Free Trade Agreement with the United States including investment opportunities in Morocco.
Dear Members of our Group
Please check first my publications on Invest and Trade in Morocco …
En Premier, vous pouvez aussi reviser mes publications sur Invest in Morocco
You can book your FREE consultation and unlock your authority-building roadmap.
or Click here on: https://forms.gle/D5zz3Lbf92wEMcu68
We will be in touch soon with FORCES
For additional information, send an email to: info@triconsultingkyoto.com
Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Ph.D. – Said Cherkaoui Ph.D. – 11/7/2024
https://triconsultingkyoto.com
https://fr.triconsultingkyoto.com
Best wishes for repeated success with TRI CK USA – California
Saidelmansourcherkaoui #Trickusa #Triconsultingkyoto
Morocco offers a promising investment landscape for foreign entrepreneurs. Here are some key reasons why investing in Morocco can be advantageous
Morocco’s economic stability, ongoing reforms, and diverse investment opportunities make it an attractive destination for international business ventures. Whether in real estate, renewable energy, tourism, or manufacturing, entrepreneurs can find promising prospects in this North African country 1.

Political Stability: Morocco benefits from a stable political environment, which is crucial for long-term investments. The government’s commitment to economic reforms is helping to boost investor confidence.

Strategic Location: Morocco’s strategic location between Europe and Sub-Saharan Africa makes it an ideal gateway for companies seeking to access both markets. The relatively low labor cost and modern infrastructure increase its attractiveness 2.

Morocco and USA Friendship since the Birth of the United States of America
As the United States was struggling in its battle for independence from Great Britain, Sultan Mohammed III of Morocco was among the first heads of state in the world to grant American ships port access. By royal decree in 1777, Sultan Mohammed III provided the Americans with an economic ally and began what would become the longest unbroken diplomatic relationship in the history of the United States. The more contemporary 2006 free trade agreement caused an increase in American and Moroccan exports from $481 million to $3.5 billion and $446 million to $1.6 billion
(Source: United States Department of State 2020 and Dylan Patrick: American Foreign Direct Investment in Morocco: How Can We Help? University of Nebraska – Lincoln
Diversified economy: The Moroccan economy is characterized by diversity and sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, services, and tourism contribute significantly to the GDP. This diversity offers diverse investment opportunities.
Real Estate Sector: Real estate in Morocco offers profitable investment opportunities. The country has seen significant growth in infrastructure development, including commercial and residential projects, resorts, and industrial zones. Cities such as Casablanca, El Jadida, Marrakech, Rabat, and Tangier offer interesting prospects for real estate investments 1.
Renewable energy: Morocco prioritizes the development of renewable energy and aims to produce 52% of its energy from renewable sources by 2030. Foreign entrepreneurs can explore investments in solar and wind energy projects, as well as in the production of energy equipment renewable. 1.
Tourism and hospitality: With its rich cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and dynamic cities, Morocco is a popular tourist destination. The tourism sector offers foreign investors the opportunity to invest in hotels, resorts, restaurants, and travel agencies. Government strategies to attract more tourists and improve infrastructure improve the growth potential of the sector 1.
![]()
Manufacturing and exports: Morocco has established itself as a manufacturing and export hub, particularly in sectors such as automotive, textiles, and electronics. Its proximity to Europe, its production costs, its competitive workforce and its free trade agreements create a favorable environment for seeking foreign entrepreneurs. Establish factories or explore export-oriented businesses 1.
Information technology and innovation: The Moroccan government actively promotes digital transformation and innovation. The growing IT sector and the startup ecosystem that supports it offer opportunities in software development, cybersecurity, e-commerce, and other technology-driven sectors.
Transition to a green economy: Morocco is a pioneer in the transition to a green economy. Ambitious energy transition plans aim to transform the country into one of the greenest and low-carbon platforms in the world 3 .
Investment incentives: The Moroccan government offers incentives to attract foreign investment, including tax exemptions, support, and simplified procedures 2.
Morocco’s economic stability, ongoing reforms, and various investment opportunities make it an attractive destination for international businesses, whether in real estate, renewable energy, tourism, or manufacturing and in this North African country you can find promising entrepreneurs.
Foreign Investment and Foreign Trade in 2024

★ Morocco has ratified 72 investment treaties for the promotion and protection of investments and 62 economic agreements, including with the United States and most EU nations, that aim to eliminate the double taxation of income or gains. Morocco is the only country on the African continent with a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the United States, eliminating tariffs on more than 95 percent of qualifying consumer and industrial goods.
★ The Government of Morocco plans to phase out tariffs for some products through 2030. The FTA supports Morocco’s goals to develop as a regional financial and trade hub, providing opportunities for the localization of services and the finishing and re-export of goods to markets in Africa, Europe, and the Middle East.
Since the U.S.-Morocco FTA came into effect bilateral trade in goods has grown nearly five-fold. The U.S. and Moroccan governments work closely to increase trade and investment through high-level consultations, bilateral dialogue, and other forums to inform U.S. businesses of investment opportunities and strengthen business-to-business ties.
According to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development’s (UNCTAD) World Investment Report 2022 , Morocco attracted the ninth-most foreign direct investment (FDI) in Africa in 2021. Inbound FDI rose by 52 percent in 2021 to $2.2 billion, vice $1.7 billion in 2020 and 2019 and a 2018 peak of $3.6 billion. France, the United Arab Emirates, and Spain hold a majority of FDI stocks.
Manufacturing attracted the highest share of FDI stocks, followed by real estate, telecommunications, tourism, and energy and mines. Morocco continues to orient itself as the “gateway to Africa,” and expanded on this role with its return to the African Union in January 2017 and the launch of the African Continental Free Trade Area (CFTA), which entered into force in 2021.
In June 2019, Morocco opened an extension of the Tangier-Med commercial shipping port, making it the largest in Africa and the Mediterranean; the government is developing a third phase for the port which will increase capacity to five million twenty-foot equivalent units (TEUs). Tangier is connected to Morocco’s political capital in Rabat and commercial hub in Casablanca by Africa’s first high-speed train service – TGV. Actually, Morocco is planning a southern connection by the TGV of Casablanca, Marrakech, Agadir, and Dakhla in the Moroccan Sahara.
Morocco’s Investment and Export Development Agency (AMDIE) ★ is the national agency responsible for the development and promotion of investments and exports. Following the reform to the law governing the country’s Regional Investment Centers (CRIs) in 2019, each of the 12 regions is empowered to lead its own investment promotion efforts. The CRI websites aggregate relevant information for interested investors and include investment maps, procedures for creating a business, production costs, applicable laws and regulations, and general business climate information, among other investment services.
Morocco actively encourages and facilitates foreign investment through a range of incentives. Here are some key investment incentives in Morocco:
Tax benefits: The Moroccan government offers tax breaks to investors, reducing the overall cost of doing business. These tax incentives apply to both foreign and local investors 1 2.
Customs Exemptions: Investors can benefit from exemptions on import duties, making it easier to import goods and materials into the country for their business operations 1.
Access to funds and grants: Morocco offers access to various funds and grants that support investment projects. These financial assistance programs aim to improve returns on investments and encourage economic growth 3.
Investment Promotion Agencies: The country has established investment promotion agencies that provide information, guidance, and support to investors. These agencies help streamline the investment process and connect investors with relevant resources 1.
Free Trade Agreements: Morocco has entered into numerous free trade agreements, providing preferential access to international markets. These agreements improve trade opportunities and make Morocco an attractive base for export-oriented businesses 1.
Morocco’s investment incentives, combined with its strategic location, political stability, and world-class infrastructure, create a favorable environment for foreign entrepreneurs looking to invest in the country 1.
Learn more 1 – state.gov 2 – moroccopreneur.com 3 – invest.advaloria.net 4 – moroccandiaspora.com
China ★ 1 Jan 2022
Said El Mansour Cherkaoui Articles on USA – Morocco Trade Relations 16 Nov 2021 In “California”
The Investment Charter, Law 18-95 of October 1995, is the current foundational Moroccan text governing investment and applies to both domestic and foreign investment (direct and portfolio).
Morocco’s Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) increased by 1.2 USD bn in June 2022, compared with an increase of 416.3 USD mn in the previous quarter. Morocco Foreign Direct Investment: USD mn net flow data is updated quarterly, available from Mar 2014 to Jun 2022.
According to data from the country’s foreign trade watchdog, the Exchange Office (OE), Morocco welcomed MAD 6.3 billion ($578 million) in investments from the US in the first half of 2022, compared to MAD 5.6 billion ($513.7 million) from France.
For the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development’s (UNCTAD) World Investment Report 2020 , Morocco attracted the eighth most foreign direct investment (FDI) in Africa. Following a record year in 2018 where Morocco attracted $3.6 billion in FDI, inbound FDI dropped by 55 percent to $1.6 billion in 2019. Despite the global COVID-19 pandemic, FDI inflows to Morocco remained largely stable totaling $1.7 billion in 2020, according to the Moroccan Foreign Exchange Office, a slight increase of one percent from the previous year. France, the UAE, and Spain hold a majority of FDI stocks. Manufacturing has the highest share of FDI stocks, followed by real estate, trade, tourism, and transportation. Morocco continues to orient itself as the “gateway to Africa” for international investors following Morocco’s return to the African Union in January 2017 and the launch of the African Continental Free Trade Area (CFTA) in March 2018, which entered into force in 2021.

In June 2019, Morocco opened an extension of the Tangier-Med commercial shipping port, making it the largest in the Mediterranean and the largest in Africa. Tangier is connected to Morocco’s political capital in Rabat and commercial hub in Casablanca by Africa’s first high-speed train service. Morocco continues to climb in the World Bank’s Doing Business index, rising to 53rd place in 2020, rising on the list by 75 places over the last decade. Despite the significant improvements in its business environment and infrastructure, high rates of unemployment, weak intellectual property rights protections, inefficient government bureaucracy, and the slow pace of regulatory reform remain challenges.
Morocco has ratified 72 investment treaties for the promotion and protection of investments and 62 economic agreements, including with the United States and most EU nations, that aim to eliminate the double taxation of income or gains. Morocco is the only country on the African continent with a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the United States, eliminating tariffs on more than 95 percent of qualifying consumer and industrial goods.
The Government of Morocco plans to phase out tariffs for some products through 2030. The FTA supports Morocco’s goals to develop as a regional financial and trade hub, providing opportunities for the localization of services and the finishing and re-export of goods to markets in Africa, Europe, and the Middle East.
Since the U.S.-Morocco FTA came into effect bilateral trade in goods has grown nearly five-fold. The U.S. and Moroccan governments work closely to increase trade and investment through high-level consultations, bilateral dialogue, and other forums to inform U.S. businesses of investment opportunities and strengthen business-to-business ties.
Doing Business in North Saharan Africa – Click on the following web link to access the slide presentation:
Doing Business in North Saharan Africa by Dr.Said El Mansour Cherkaoui

Click on the following web link to access the slide presentation:
Doing Business in North Saharan Africa by Dr.Said El Mansour Cherkaoui



Trade of United States, California with Morocco
The Moroccan-American friendship up-to-this date [2019] has lasted
USA and Morocco: Trade Profile
Dr. Said El Mansour Cherkaoui has organized several trade missions in California, North and Sub Saharan Africa, China, France and Spain. Similarly, he has contributed in the setting of trade relations within the scope of the US – Morocco Free Trade Agreement (MAFTA). Dr. Cherkaoui’s profile can be accessed at this link: https://www.linkedin.com/in/drsaidcherkaoui/ Morocco Background The… Read More USA and Morocco: Trade Profile
With an annual Gross Domestic Product growth rate of nearly five percent over the past five years, Morocco’s recent economic history is one of macroeconomic stability and low inflation, despite the challenges of the Arab Spring. In the World Bank’s 2017 Doing Business report, Morocco’s rating improved to 69th in the world. Morocco is conveniently located for investors interested in exporting to Europe and Africa. Moreover, the availability of skilled and competitive labor at lower costs, relative to Europe, is a key factor in attracting automakers to Morocco. These automakers are also eligible for tax exemptions for 25 years, provided that most of the production is destined for export.“
The interests of Renault in Morocco remain the control of the Moroccan automobile market, the availability of very affordable and relatively well-educated workforce, and the bridge to Europe and the Gateway to Africa and the Middle East that Morocco provides through its strategic geographical location. Additional benefits can be also the unique opportunities that are offered by the operation of Tangier. Renault is currently the dominant company in the Moroccan automotive market. The Dacia and Renault brands, owned and operated by Renault, represent respectively 20% and 17% of the market. Renault is already operating a plant in Casablanca and the increased production of this new plant will allow the company to maintain its market share as the Moroccan automotive industry grows.” (Said El Mansour Cherkaoui)
Morocco Tourism Investment Road Show to the U.S.
WHEN: January 25, 2018 – January 26, 2018 all-day – WHERE: Los Angeles, CA – USA

The Morocco Free Trade Agreement (MAFTA)
The Morocco Free Trade Agreement (MAFTA) went into effect on January 1, 2006. Under the agreement most Moroccan goods enter the United States duty-free and virtually all will enter free by the time it is fully implemented on January 1, 2023. The Morocco FTA does NOT provide a merchandise processing fee (MPF) exemption.

Value proposition: Read more on the attractiveness of Morocco for Foreign Direct Investment
Morocco Free Trade Agreement (MAFTA)
Information for U.S. Exporters is available through the Department of Commerce at:
http://www.export.gov/FTA/index.asp
The Morocco Free Trade Agreement (MAFTA) went into effect on January 1, 2006. Under the agreement most Moroccan goods enter the United States duty free and virtually all will enter free by the time it is fully implemented on January 1, 2023. The Morocco FTA does NOT provide a merchandise processing fee (MPF) exemption. To learn more about how to claim preference on these goods, select the following:
Morocco Free Trade Agreement Implementation Instructions
This document provides the most relevant information in HTSUS General Notes 27 and 19 CFR Subpart M.
Data Elements for the Morocco FTA Certificate of Origin – Attachment A
This certification can be used by Moroccan producers and exporters, and US importers, when attesting that their goods meet the requirements of the Morocco FTA.
Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States (HTSUS) – Morocco FTA General Notes 27
General note, including the General Rules of Origin, Definitions, Value (including Regional Value Content and De Minimis), Sets, Packing and Packaging Materials, Indirect Materials, Record keeping and the all-important Product Specific Rules of Origin
NOTE: On the USITC link, select the “General Notes; General rules of Interpretation; General Statistical Notes,” link, followed by “General Notes 27”.
The following Morocco FTA goods may be subject to a reduced tariff rate quota (TRQ): beef; dairy; dried onions; dried garlic; peanuts; tomato paste, puree and sauce; tobacco; cotton; fabric and apparel.
Click here for an overview of quota. Go to the Commodity Graph Report for current fill levels. Go to the TPL Threshold to Fill List to see almost closed and closed quotas.
Reconciliation
The Reconciliation Prototype is unavailable for post-importation Morocco FTA claims because they are not administered under 19 USC 1520(d) but as Post Entry Amendments (PEAs), Post Summary Corrections (PSCs) or Protests (19 USC 1514, 19 CFR 174).
Morocco is also pursuing its own opening economic strategy, developing its trade relations with regional economic communities in Africa .. More to read at this link: Integration of Africa with Morocco
Additional Resources and Regulations:
Trade in Goods with Morocco
U.S.-Morocco Free Trade Agreement Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
- Morocco FTA Text – Complete text of the agreement.
UNITED STATES – MOROCCO FREE TRADE AGREEMENT
- Morocco FTA Regulations
- e-CFR website including Import Requirements, Filing a Claim, Regional Value Content (RVC) Certification, Post-Importation Refunds, Rules of Origin, Origin Verifications, Transshipment, and Penalties.
- USITC Publication 3721
- Includes the modifications to the HTSUS, the Duty Phase-Out Schedule, and other important information.
- Morocco FTA Implementation Act—House Report
- House Report 108-627, United States-Morocco Free Trade Agreement Implementation Act, 108th Congress, 2nd Session
- Presidential Proclamation 7971
- Enacts the Morocco FTA; Published in the Federal Register on December 27, 2005.
- Morocco FTA Summaries and Reports
- Made available by the United States Trade Representative (USTR).
Last published: November 16, 2017
Additional information is available at the US Department of Commerce, International Trade Administration and the Department of Justice in Washington, DC., Marketwired (August 17, 2016) and World Bank, BEA.
Editor: Said El Mansour Cherkaoui, Ph.D.
US Aid to Morocco: Olive and Agricultural Products
In 2004, Congress created the Millennium Challenge Corp., a foreign aid agency headed by the secretary of state, to help developing countries reduce poverty. Since its inception, the agency has authorized grants totaling more than $7 billion to help 23 African and Latin American countries.
In 2007 the agency agreed to give Morocco $697.5 million over five years to improve the country’s employment rate and salaries by investing in its fruit-tree farms, small-scale fisheries, and artisan crafts, according to Millennium. Nearly half of that money – $320 million – is earmarked for the Fruit Tree Productivity Project, with 80 percent of the cash going to olives and the rest to improve date, fig, and almond production. Dates, figs, and almonds are also key California crops.
U.S. aid to Morocco worries California olive farmers
September 18, 2011 | Stacy Finz
Patrick Fine, who oversees such agreements as Millennium’s vice president of compact operations, said he does not believe that the investment in Morocco will harm California producers. … Not meeting demand “I …
Patrick Fine, who oversees such agreements as Millennium’s vice president of compact operations, said he does not believe that the investment in Morocco will harm California producers. The project, he said, is designed to help poor rural families increase their incomes and to help develop a strong ally in an important region in the world.




Leave a Reply